BREATH FOR DX
The BreathForDiagnosis consortium combines expertise from academia, NGOs, and industry. It includes experts in the development of diagnostics, partners with extensive expertise in implementation science, including mixed-methods research approaches, cost-effectiveness, and modelling. The studies will take place in four countries: South Africa, Germany, Italy, and Romania.
Respiratory infections resulted in over seven million deaths in 2020 and were responsible for seven out of nine pandemics in the 20th century. Aerosol transmission of respiratory infections has been largely underestimated, with the COVID-19 pandemic highlighting the limitations of traditional views of droplet and fomite transmission. Moreover, respiratory infections such as tuberculosis (TB) and COVID-19 have a propensity to disproportionately affect underprivileged populations and those with low socioeconomic status, including vulnerable populations. Improving early detection of respiratory infections is key to improving both individual and public health. Current diagnostic sampling methods for respiratory infections are flawed. Sputum is often difficult to obtain and transport and has suboptimal sensitivity for many respiratory pathogens. Production of sputum varies according to pathogen and individual immune response, and methods to induce sputum are resource consuming and not scalable. Based on current evidence, exhaled breath aerosol (XBA) is a non-invasive, easy to collect sample for detection of respiratory infections.
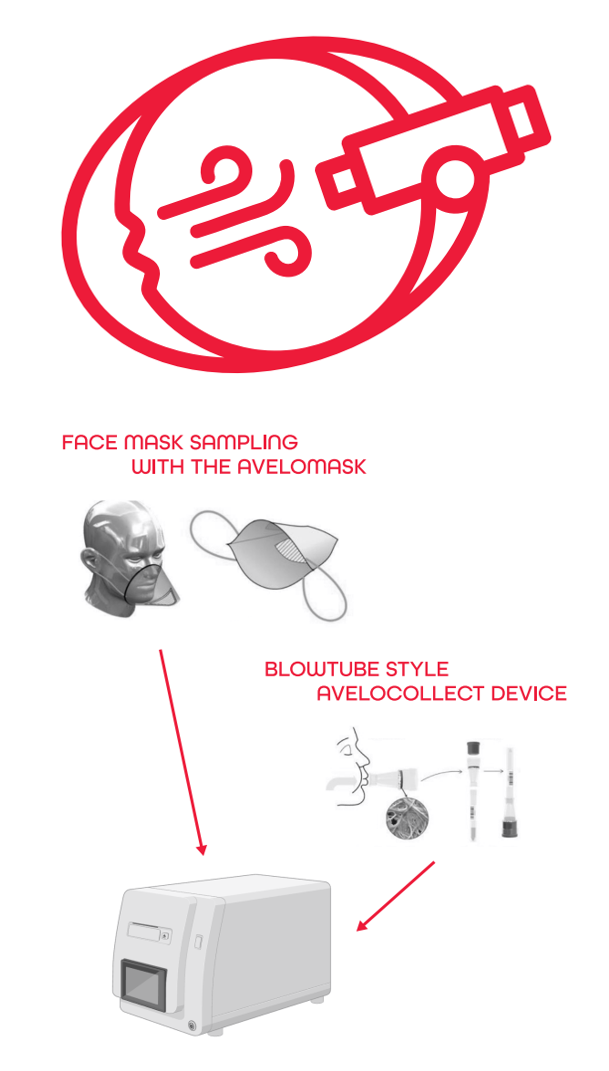
The overall aim of the BreathForDiagnosis project is to establish XBA as a novel, non-invasive sample type using innovative, scalable point-of-care sampling devices and to generate evidence for diagnosis, screening, and antimicrobial resistance detection use cases. Our project will go beyond the current state-of-the-art for breath sampling and diagnosis by optimising, validating, and testing two simplified, fast, and scalable XBA sampling devices. The two sampling devices are shown on the right.